What is the idea of Hazard?
- Volcanic Hazards
- Seismic Hazards
- Tempest Hazards
- Out of control fires
What is the Concept of Hazard?

A Hazard is something that is a potential risk to human life or property. A characteristic hazard is an apparent occasion that compromises both life and property. They regularly bring about debacles that cause some death toll or potential harm to the constructed condition and make extreme interruption to human exercises. Regular Hazards are brought about by characteristic procedures and be partitioned into three kinds:
- Geophysical hazards-Caused via Land Processes

These incorporate quakes, volcanic emissions, avalanches and torrents
- Atmospheric Hazards-Caused by Climatic Processes.
These incorporate tropical tornados, storms, dry seasons, boundaries of blistering or chilly climate and out of control fires.
- Hydrological Hazards-Caused by Water Movement
These incorporate floods and torrential slides
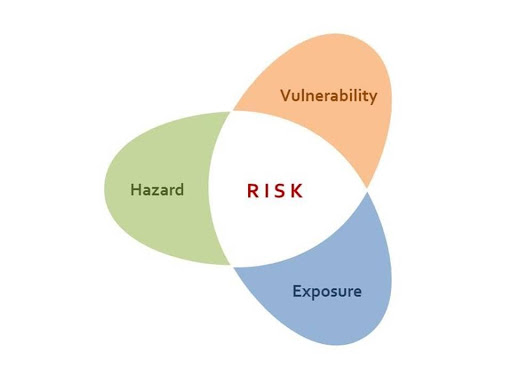
Risk: When a hazard entirely influences people
Hazard: The Likelihood that a hazard will genuinely influence people.
Vulnerability: How powerless a populace is to the harm brought about by a hazard
Hazards can have critical effects while they are happening and regularly need and crisis reaction (e.g. emptying a region). The effects can likewise continue for quite a while after the hazard itself has passed.

Hazard and Vulnerability:
Hazard is the introduction of individuals to a hazardous occasion showing a potential danger to themselves, their assets and the assembled condition wherein they live. Individuals, however, deliberately put themselves in danger from characteristic hazards, and the inquiry must be the reason do they do it?
Potential reasons incorporate the accompanying:
Hazard occasions are eccentric: We cannot foresee the recurrence, extent or size of a characteristic occasion.
Absence of choices: Due to social, political, monetary and social components, individuals cannot just evacuate themselves starting with one spot and move then onto the next, surrendering their homes, land and work.
Changing the degree of a hazard: Places that were once generally safe may have become, through time, unquestionably to a higher degree a hazard. Deforestation, for instance, could bring about all the more flooding from torrential downpour related to hurricanes, and there could likewise be a more severe hazard from avalanches.
Cost/advantage: Numerous hazardous territories offer focal points that in individuals’ psyches exceed the hazard that they are taking. Californian urban communities, for instance, have a high hazard from seismic tremors, yet individuals see the numerous points of interest in living there as more prominent than the potential hazard.
Perception
Defenselessness to physical hazards implies the potential for misfortune. Since misfortunes change topographically after some time and among various social gatherings, weakness hence likewise shifts after some time and space.
Hazard is diverse to individuals in various regions. A comparable measured characteristic hazard occasion can have generally changing effects in various pieces of the world. Individuals’ riches and the degree of innovation that they can apply do influence how much the hazard occasion will affect them.
More extravagant individuals and nations can ensure themselves by structures of ocean protections, developing safe tremor structures, giving better crisis administrations, and so forth. They can likewise be better arranged by being made increasingly mindful of the hazard through training. The individuals of urban areas in less fortunate nations are progressively powerless.
Accordingly, urban regions have developed an ever-increasing number of individuals who have been compelled to live in hazardous territories, for example, hillsides that are inclined to landslides, and in the most reduced lying parts where they are in danger from typhoons and torrents.
What is the view of common hazards?
Individuals respond to the risk of hazards in various manners due to how people get and process data. For instance, a few people accept they will never encounter a specific hazard, others adjust their way of life to limit hazards, and others acknowledge hazards as being outside their ability to control.
Recognition is affected by their financial, social and social foundation.
Financial status-Richer individuals might have the option to bear to move to territories that are less inclined to hazards or to construct their homes to withstand hazards so that they may see the hazard as littler.
Level of instruction, e.g., with individuals who have more training, may have a superior comprehension of the dangers of hazards, or they may accept that they can lessen the dangers or relieve the effects.
Religion, social/ethnic foundation, e.g., a few people see hazards as demonstrations of God, sent to rebuff individuals.
Past experience-e.g., individuals who live in hazard-inclined zones may have encountered hazards previously, which may influence the apparent hazard from future hazards.
Qualities, character and desires, e.g., a few people dread hazards and others may consider them energizing.
View of a hazard will, at last, decide the game-plan taken by people to change the occasion or the reactions they anticipate from governments and different associations.
There is regularly an incredible contrast in the impression of a hazard between individuals of varying degrees of financial advancement. In wealthier regions, there is a feeling that the better that you are educated about hazards, the more capable you will be to withstand the effect of the hazard and maybe even keep the fiasco from occurring. This is typically founded on government and network activity and is upheld by capital that will fund innovatively based arrangements. The feeling of powerlessness, even with usual hazards, will, in general, increment with the degree of neediness and the hardship of the individuals. Indeed, even in wealthier nations, there are gatherings of burdened individuals who will in general view regular hazards as a feature of their lifestyle, as they are viewed as unavoidable, similarly as the more significant part of individuals in more unfortunate nations see the effects of these occasions s being a piece of the states of neediness.

Individuals may see characteristic hazards in accompanying manners:
Resignation (acknowledgment): Such hazards are regular occasions that are a piece of living in a zone. A few networks would venture to state that they are ‘Divine beings will.’ Activity is in this manner, ordinarily immediate and worried about wellbeing. Misfortunes are acknowledged as unavoidable, and individuals remain where they seem to be.
Adaption: People see that they can get ready for, and in this way, endure the event(s) by expectation, avoidance, as well as security, contingent on the monetary and innovative conditions of the zone being referred to.
Dread: The view of the hazard is with the end goal that individuals feel so defenceless against an occasion that they are never again ready to confront living in the region and move away to districts appear to be unaffected by the hazard.
Reacting to Hazards
People and Governments may react to a hazard to attempt to lessen their weakness or to decrease its effects.
The characteristic human reaction to a hazard is to decrease hazard to life and value. At a neighbourhood level, this includes sparing belongings and defending property; all around this implies planning salvage and compassionate guide. The force and size of the occasion just as the first condition of the foundation (and how gravely it has been harmed) influences the speed of the global reaction.

Individuals react to typical hazards and the dangers that they can present by looking for approaches to decrease the hazard. Reactions can emerge out of people, the nearby network with individuals cooperating, and from national governments and global organizations.
Network versatility is the continued capacity of a network to use accessible assets to react to, withstand and recoup structure the impacts of regular hazards. Strong networks can limit the impacts of a hazard, making the arrival to ordinary life as easy as could be allowed.
The Park Response Model
The recreation center model shows the various periods of reaction to a hazard.
The Disaster/Response Curve shows that hazard occasions can have shifting effects after some time; in 1991, Park formulated his effect/reaction model.
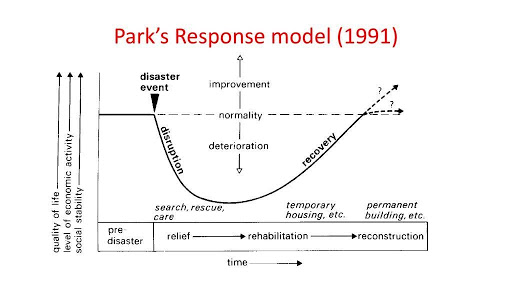
The Park model shows how reactions progress during a debacle, which may enable organizers to foresee what assets will be required at each stage. The model can likewise assist organizers with preparing for future hazard occasions. For instance, the remaking period of the model shows that conditions can be improved after a catastrophe, (e.g. by structuring hazard safe structures or introducing cautioning systems), which will assist with moderating the effects of future hazard occasions.
Before the calamity strikes, where personal satisfaction is typical for the region. Here individuals attempt their best to forestall such occasions and get ready if they ought to occur.
(Disturbance)- During and legitimately, after the hazard occasion happens, there is demolition of property, the death toll, and so forth. Personal satisfaction out of nowhere drops with potential individuals making a quick move to save lives and, if conceivable, the fabricated condition.
Help, where restorative consideration, salvage administrations, and generally speaking consideration are conveyed. This can last from a couple of hours to a few days if the occasion has been harming. Starting here, the personal satisfaction of the individuals of the territory starts to increment gradually.
Restoration, Once the immediate effect is levelled out, individuals begin to determine long haul issues. Where individuals attempt to restore the situation to typical by giving nourishment, water and safe house for those generally influenced, this period can last anything from a couple of days to weeks.
Remaking, where the foundation and property are
Remade and crops regrown. As of now, individuals utilize the experience of the occasion to attempt to figure out how to all the more likely react to the following one.
A vital component of the cutting-edge way to deal with hazard reaction is that hazards are best fought by effective administration. Present-day the board procedures, with their social event of data, careful examination and watchful arranging, expect to make the most effective utilization of the cash accessible to go up against characteristic hazards. A procedure is known as coordinated hazard the executives are regularly utilized, which consolidates distinguishing proof of the hazard, examination of the dangers, setting up needs, treating the hazard and actualizing a hazard decrease plan, creating open mindfulness and a correspondence system, and checking and auditing the entire procedure. The legislatures of numerous nations utilize such plans.
Individuals and associations, along these lines, attempt to oversee characteristic hazards in the accompanying manners:
Expectation: It might be conceivable to give admonitions that will empower a move to be made. The way into this is improved checking to give expectations, which implies that alerts can be given. The National Hurricane Center in Florida is a genuine case of an office.
Showing how expectation can rely upon checking, using data from satellites and land-, ocean and air-based chronicles.
Avoidance: For common hazards, this is most likely ridiculous even though there have been thoughts and even plans, for example, seeding mists in potential typhoons to cause more precipitation, which in principle would bring about a debilitating of the framework as it approaches land.
Insurance: The point is to ensure individuals, their assets and the manufactured condition from the effect of the occasion. This typically includes changes to the fabricated condition, for example, improved ocean dividers and seismic tremor verification structures. One manner by which governments can act, and individuals respond, is to attempt to change perspectives and practices to typical hazards which will lessen individuals’ helplessness. Network readiness (or chance sharing) includes prearranged measures that intend to lessen the death toll and property harm through state-funded training and mindfulness programs, departure strategies and arrangement of crisis restorative and nourishment supplies and havens. There can likewise be endeavours to alter misfortunes through protection (more extravagant territories) and global air (in less fortunate locales).
All endeavours at the board must be assessed as far as their prosperity. Fruitful plans incorporate the utilization of explosive to redirect magma streams on Mt Etna and pouring ocean water on magma streams in Iceland. Then again, the Japanese felt that they were solid and steady for quakes, but in 1995 the city of Kobe endured the Great Hanshin seismic tremor, which wrecked more than 100,000 structures (with multiple times that number harmed) and a loss of life of more than 6,000 with 35,000 wounds.
Read more about Climatic Hazards
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the definition of a hazard in geography?
In geography, a hazard is a potentially dangerous natural or human-induced event that threatens people, property, and the environment.
How are hazards classified in geography?
Hazards can be classified as natural (earthquakes, floods) or human-made (pollution, industrial accidents), and further categorized by their impacts and frequencies.
Why is studying hazards important for geography?
Studying hazards helps us understand their causes, distribution, and impacts, enabling better preparedness, response, and mitigation strategies.
What is the difference between a hazard and a disaster?
A hazard is a potential threat, while a disaster is the actual occurrence of a hazardous event causing significant damage, loss, and disruption.
How do geographers contribute to hazard management and mitigation?
Geographers assess vulnerability, analyze spatial patterns, and recommend strategies for minimizing hazard impacts through land-use planning, early warning systems, and education.
References
- AQA A Level Geography: Hazards – The Concept of a Hazard in a Geographical Context. (n.d.). Retrieved from tes: https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/aqa-a-level-geography-hazards-the-concept-of-a-hazard-in-a-geographical-context-12144525
- Concept of Hazard in Geographical Context . (n.d.). Retrieved from WattPad: https://www.wattpad.com/679360903-hazards-a-level-geography-concept-of-hazard-in/page/3
- natural disasters and hazards. (n.d.). Retrieved from wiki.seg: https://wiki.seg.org/wiki/Natural_disasters_and_hazards
- natural hazard. (n.d.). Retrieved from wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_hazard
- Responding to Natural Disasters: Rowing Against a Fast-Rising Tide of Risk. (n.d.). Retrieved from MEI: https://www.mei.edu/publications/responding-natural-disasters-rowing-against-fast-rising-tide-risk
- TECTONIC PROCESSES AND HAZARDS . (n.d.). Retrieved from Slide Player: https://slideplayer.com/slide/14091206/What is the difference between a ‘hazard’ and a ‘risk’? (n.d.). Retrieved from Worksmart: https://worksmart.org.uk/health-advice/health-and-safety/hazards-and-risks/what-difference-between-hazard-and-risk
