Tourism is a journey commenced for goals of recreation rather than a business. It has become the world’s sole biggest tertiary activity in total recorded jobs (250 million) and total income (40 per cent of the total GDP). Besides, many regional persons, are engaged in services like accommodation, refreshments, transportation, recreation and specialised shops attending the tourists. Tourism promotes the increase in infrastructure businesses, retail dealing, and craft businesses (souvenirs). In some regions, tourism is periodical because the vacation period is reliant on pleasant weather situations, but many areas attract visitors all the year round.
Tourist Areas
The warmer regions around the Mediterranean Coast and the West Coast of India are some of the famous tourist spots in the world.
Others involve winter sports areas, found largely in mountainous regions, and several scenic terrains and national parks, which are dispersed. Historic towns also entice tourists, because of the monument, cultural activities and heritage sites.
Factors Influencing Tourism
Demand: Since the last century, the desire for holidays has risen rapidly. Rises in the standard of living and expanded leisure time, allow many more people to go on vacations for relaxation.
Transport: The opening-up of tourist regions has been supported by an improvement in transport facilities. Travel is comfortable by car, with high-grade road systems. More notable in recent years has been the development of air transport. For example, air travel enables one to travel everywhere in the world in a few hours of flying time from their place. The appearance of package holidays has decreased the costs.
Tourist Attractions
Climate: Most people from colder areas expect to have a mild, sunny climate for beach holidays. This is one of the central rationales for the importance of tourism in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean lands. The Mediterranean environment gives relatively consistently higher temperatures than in other parts of Europe, long period of sunshine and less rainfall during the peak holiday season. People buying winter holidays have particular climatic demands, either higher temperatures than their own countries or snow cover fit for skiing.
Landscape: Many people like to spend their vacations in a beautiful surrounding, which usually means mountains, lakes, panoramic sea coasts and landscapes not completely changed by man.
History and Art: The art and history of a region have the potential to attract tourists. People visit old or scenic towns and archaeological sites and fancy searching castles, churches and palaces.
Culture and Economy: These bring tourists with an affinity for experiencing ethnic and social customs. Besides, if a country provides for the requirements of tourists at a reasonable cost, it is likely to become very famous. Home-stay has risen as a lucrative business in cities such as London.
Models for development in tourism
Butler model is a model for tourism development which displays how tourists in a specific region can grow. The model takes into account a resort which is within the location of the tourist spot. Butler showed that all the resorts undergo the same process. It can be explained through seven stages.
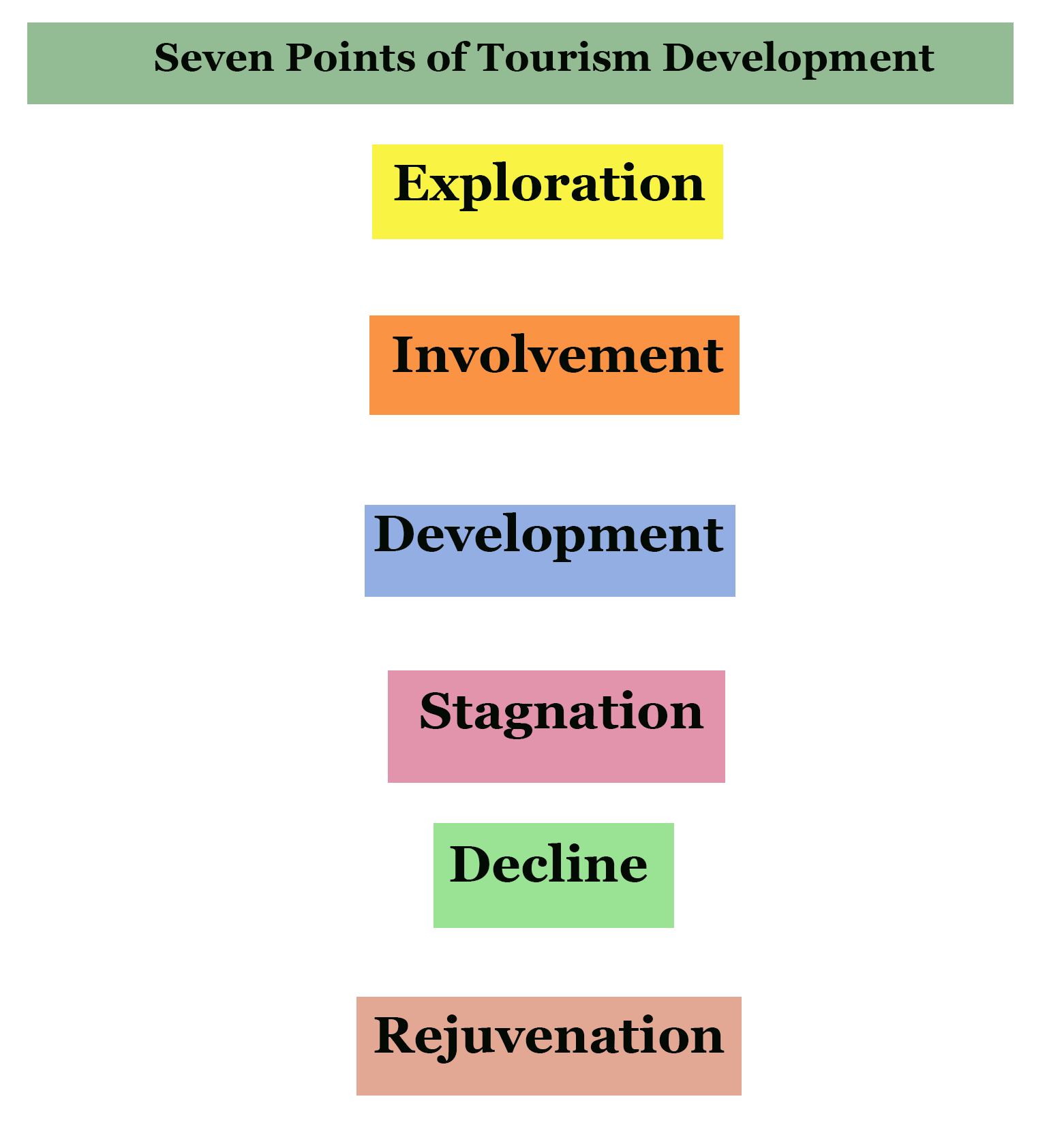
The seven points of tourist development
- Exploration – Initially, a very small number of tourist come to visit the tourist spot. The area is unexploited and there are very few tourists facilities that are available.
- Involvement – The local people begin to give some facilities for tourists and the recognition of the area as tourist spot begins for a particular season.
- Development – The country as a whole recognises the importance of that location and advertise and develop the area and hence the location gets recognised as a tourist destination.
- Consolidation – The region keeps attracting the tourists and the increase in the number of tourists does not remain as fast as it was in the beginning. The conflict between and hosts and tourists arises.
- Stagnation – the depreciation in the infrastructure leads to the decline in the facilities for tourists and consequently the decline in the number of tourists is seen.
- Decline – At the point of stagnation, if the resort does not rebuild or renovate its facilities, it declines. Hence, the people employed in the area lose their jobs and the reputation of the region deteriorates further.
- Rejuvenation – Again, when the government and the local people again make efforts to invest and modernise the area and better the facilities, the tourists again start to increase in number.
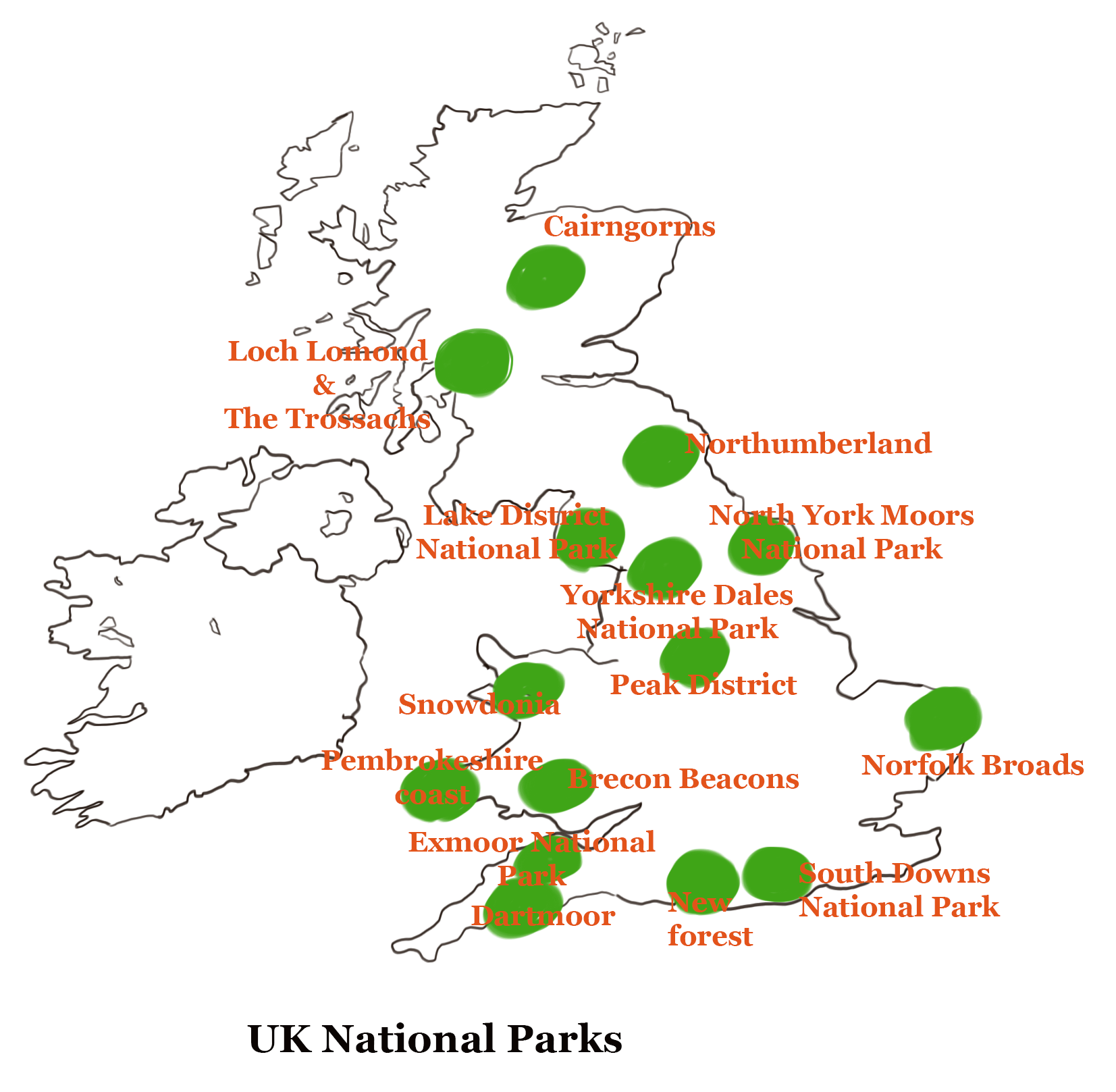
National Parks in the UK
The responsibility of national parks is given to countries within which the territory of the park falls. They have their own arrangements and policies. Overall, there are around 15 national parks in the UK, of which 10 are in England, 3 in Wales and 2 in Scotland. These parks are not national parks in the true sense if you analyse them according to the standards accepted by IUCN. However, they are regions of the outstanding landscape where residency and commercial activities are restricted.
These national parks have 2 statutory (enacted by law) purposes:
- Conservation and enhancement of the natural and cultural heritage of the region.
- Promotion of understanding and recreational qualities of the national parks for the public.
The national parks in Scotland have two more statutory objectives:
- Promotion of sustainable utilisation of natural resources in the region.
- Promotion of the sustainable social and economic development of the region’s communities.
All of these national parks are members of National Parks, UK, which work for the promotion of the national parks and to smoothens the training and development process among members and staff of all the national parks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key factors that contribute to the development of tourism in a region?
Factors include natural attractions, cultural heritage, infrastructure, marketing efforts, political stability, and government policies promoting tourism.
How can sustainable tourism development benefit both the environment and local communities?
Sustainable tourism minimizes negative environmental impacts, supports conservation efforts, and provides economic benefits to local communities through responsible tourism practices.
Describe the different stages of tourism development, from exploration to mass tourism.
Stages include exploration, involvement, development, consolidation, stagnation, and decline, with each stage representing varying levels of tourist arrivals and infrastructure development.
What role does ecotourism play in responsible tourism development, and how does it promote environmental conservation?
Ecotourism focuses on nature-based experiences while emphasizing environmental conservation and community involvement, helping protect fragile ecosystems.
How can tourism development impact the preservation of cultural heritage, and what are the challenges associated with cultural tourism?
Tourism can help preserve cultural heritage by generating revenue for its maintenance. Challenges include managing visitor impacts and ensuring the authenticity of cultural experiences.