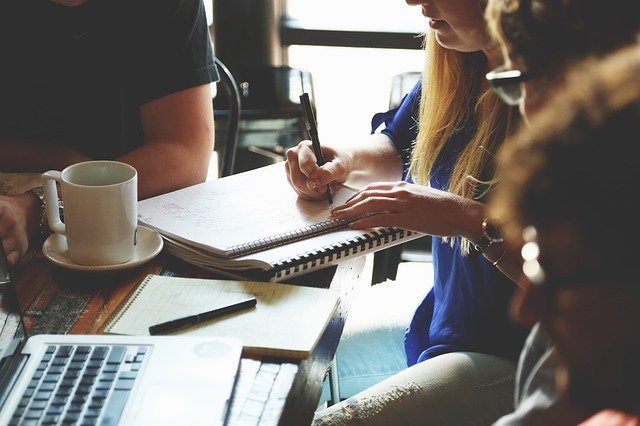
The Tertiary Industry connects directly with the Primary and Secondary Sectors but plays a different and unique role. This industry provides the necessary services after the collection and refinement of raw materials. Services include education, transportation, health service, finance, sales, retail, tourism and entertainment. For example, if a person sells you an investment or an organisation helps you in a financial decision-making process.
The Primary and Secondary Industries focus on the tangible aspects of the economy. While the Tertiary Industry aims to provide a service. For example, this industry does not provide you with a specific product, a ring. It rather uses a person to sell you the jewellery.
Also, if you become sick and need to see a doctor. The doctor provides you with a service by checking on your health status. This service presents an aspect one cannot necessarily rate according to something tangible.
The Tertiary Industry focuses significantly on supporting the other sectors. If you work at a vehicle manufacturing plant, you need some method to reach your workplace. This means you need a service provider to take you to work.
Tertiary Industries comprise many opportunities within the services environment. It also contains different positives and negatives. The Tertiary Industry can become extensively fragile in the event of an economic decline. These downturns generally impact a country’s ability to grow the Tertiary Industry. Let us see in the following sections what it means.
Check out our GCSE and A-Level Teaching Materials on Tertiary Industries
What are Tertiary Industries?
Tertiary Industries and sectors refer to economically active countries that focus on sales and the use of diverse goods and services. They aim to operate mainly within a service industry environment. Some economically advanced countries include the UK, the USA, Germany, Japan, and France.
The Tertiary Industry focuses on a component of an economy that provides services to its consumers. These involve a large range of opportunities for example schools, restaurants, or financial banks. Usually, when countries become more developed, they tend to focus on their tertiary sectors. Tertiary Industry types aim to provide a specialised service bought by a customer or organisation.
What types of Tertiary Industries exist?
The types of Tertiary Industries work within a specific space aligned with business-related activities. These types of industries refer to rail transport, road transportation, or shipping services. It also speaks to taxi services, hotels, recreational lodges, hospitality, and restaurants. Other services include clinics, veterinarians, banks, and investment specialists. The service expanded significantly by allowing different subject specialists to provide a service in consulting. For example, people use their skills to provide institutions or other individuals with advice. We see this as a service without selling a specific tangible product.
What are the characteristics of Tertiary Industries?
The Tertiary Industry comprises two different sectors. The first component focuses on the financial sectors or businesses that aim to reproduce capital. The second component aims to provide services in the non-profit environment, for example, in government institutions. This sector purely focuses on providing access to services. Meaning this industry only supplies a person or organisation with help to process financial transactions, for example. They do not supply any goods or products.
Tertiary Industries maintain connections with the Primary as well as the Secondary Industries. For example, the shipping industry transporting goods to another country needs an update from the weather services for safety reasons. Depending on a country’s characteristics, these Tertiary Industries form part of society’s daily lifestyle. One needs to go to school, visit the shop, withdraw cash at the bank or speak with a doctor.
The Tertiary Industry provides many positives to the economy and supports a country’s objectives to develop. These key positives involve the following:
- The Tertiary Sector allows for the development of large-scale employment opportunities in different fields. The economic sector normally provides significant opportunities for people who work in the Tertiary Industry. Just think about the banks, how many people they employ, or the hospitality sector.
- This sector continues to grow and remove the concentration from primary activities. Countries aim to move away from total reliance on the primary industries to innovation and service-focused opportunities. The UK achieved significant success in the field by developing post-industrial opportunities. As much as you need primary and secondary sectors to collect raw materials and refine them, you also need services. For example, you require services to transport your workers to the manufacturing plant.
- It allows the ability for people to specialise their skills in the services environment. Different individuals comprise varied talents and some people may perform better in a service environment.
The Tertiary Industry consists of diverse challenges, especially during the sale of the product.
Some of these concerns relate to the following:
- The alignment of a price with an intangible product offers great difficulties and sometimes dissatisfaction during the transaction. One person or organisation’s idea about the value of the service may differ from the other.
- The quality of the service becomes debatable and questions are raised regarding the mathematical explanation of product quality. The problem remains with selling a product you cannot see or touch.
- The provision of services sometimes becomes complex because of external factors. For example, the person providing a service may be distracted by something and prevented from focusing. It subsequently results in the person not performing. The intangible aspect becomes difficult to manage as a service mostly because of human involvement.
- The Tertiary Industry remains sensitive toward the occurrences of economic or social instability. If a country experiences diverse challenges, these might impact its ability to grow the primary or secondary sectors. It subsequently influences the tertiary component as well.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main sectors in the Tertiary Industry environment?
The main factors in the Tertiary Industry relate to their ability to provide a service. They prevent focusing on the production of tangible goods. The aim of the tertiary sector relates to giving a service or helping individuals or organisations. This sector creates no tangible products.
Is the Tertiary Industry typical of a developing or developed country?
The Tertiary Industry generally becomes stronger in developed countries. Although in developing countries, the services also occur. In developed countries, a larger focus becomes available, for example, with the expansion of the financial, economic and hospitality services.
What are the effects of the Tertiary Industry on the economy of a country?
The Tertiary Industry plays a key role in expanding the economy of a country. The focus remains on providing the country’s alternative industries with constant support. The growth in the support sector usually displays a significant expansion of the global and local economic status. It also allows the country to expand its services across its borders and assist other countries.
Can we live without the Tertiary Industry?
Countries require the Tertiary Industry to maintain the support systems to their Primary and Secondary Industries. The size of the Tertiary Industries varies depending on the services provided and the status countries comprise.
Is the Tertiary Industry experiencing threats?
The Tertiary Industry experiences threats when the economy struggles. Countries subsequently revert to the Primary and Secondary Industries to remain stable. During these instances, one notices a decline in financial statuses, investment and consultancy services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What defines the tertiary industry sector?
The tertiary sector involves providing services rather than producing goods, encompassing areas like retail, hospitality, healthcare, finance, and entertainment.
A hotel or hospitality establishment falls within the tertiary sector, providing accommodation and services to travellers.
How does healthcare fit into the tertiary industry?
Healthcare services, including medical care, hospitals, and clinics, are integral components of the tertiary sector, ensuring public health and well-being.
What role does the entertainment industry play in the tertiary sector?
The entertainment industry, including theatres, sports venues, and media outlets, provides recreational and cultural services to consumers.
How does e-commerce relate to the tertiary sector?
E-commerce platforms and online retail businesses are part of the tertiary sector, offering digital and physical goods and services to customers.
References
- https://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/oi/authority.20110803103229864
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/t/tertiaryindustry.asp
- X. Liu, “Empirical Research on the Contribution to the Tertiary Industry of Modern Service Industry,” 2011 International Conference on Information Management, Innovation Management and Industrial Engineering, Shenzhen, 2011, pp. 3-5.