When it comes to showing equality, the dictionary defines equality as “the state of being equal, especially in status, rights, and opportunities”. To measure and qualitatively describe equality, two methods can be used: The Lorenz Curve and the Gini Coefficient.
Showing Equality – The Lorenz Curve
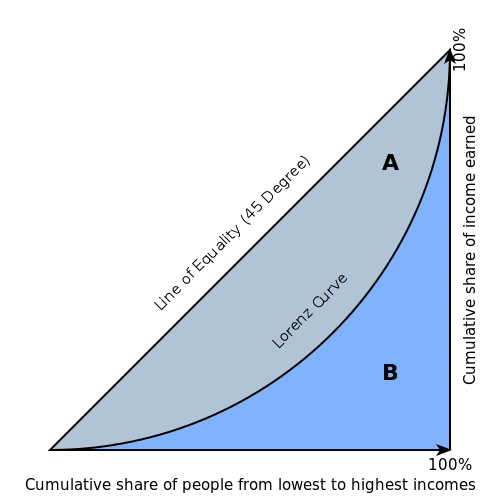
The Lorenz curve is a graphical representation of income inequality or wealth inequality developed by American economist Max Lorenz in 1905. It is a graphical representation of the distribution or equality of something. In the graph, The percentage of households is plotted on the x-axis, the percentage of income on the y-axis. The straight line from (0,0) to (100,100) shows perfect equality, whereas the line from (0,0) to (0,100) shows perfect inequality. The line drawn between these two lines is the actual measurement. The graph below shows an example of a typical Lorenz Curve:
Gini Coefficient
The Gini coefficient is a measure of inequality in a distribution developed by the Italian statistician and sociologist Corrado Gini. This coefficient gives a statistical number to measure inequality rather than a graphical display. The Gini coefficient is always measured between 0 and 1. A measurement of zero indicates perfect equality, while a measurement of one indicates maximum inequality. It is the lightly shaded blue area of the curve and the higher the Gini coefficient the higher the inequality.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is equality defined in the context of human geography?
In human geography, equality refers to the fair and just distribution of resources, opportunities, and outcomes among individuals and groups within a society or geographic area. It encompasses social, economic, and political aspects, aiming to eliminate discrimination, disparities, and systemic barriers.
What are some indicators used to measure equality in human geography?
Various indicators can be used to measure equality in human geography. These include assessing the distribution of income and wealth among different social groups and regions, examining disparities in access to quality education and educational outcomes across different demographics, analyzing disparities in employment rates, types of employment, and wage gaps between different social groups, examining disparities in health outcomes, access to healthcare facilities, and quality of healthcare services, and assessing the representation of diverse social groups in decision-making processes and political institutions. These indicators help shed light on the extent of equality or inequality within a given society or geographic area.
How does spatial inequality manifest in human geography?
Spatial inequality refers to the unequal distribution of resources, opportunities, and outcomes across different geographic areas. It can be seen in disparities such as uneven development, access to basic services (e.g., water, sanitation), infrastructure (e.g., transportation, communication), and socioeconomic conditions between urban and rural areas or between different regions within a country.
What are some strategies for promoting equality in human geography?
Strategies for promoting equality in human geography encompass various approaches. These include reducing discrimination and biases through policies and laws that safeguard the rights of marginalized groups, enhancing access to quality education and healthcare for individuals irrespective of socioeconomic background or geographic location, implementing affirmative action or quota systems to foster equal representation and opportunities for underrepresented groups, investing in infrastructure and services in marginalized or disadvantaged areas to uplift living conditions and encourage economic development, and promoting inclusive urban planning that takes into account the needs and aspirations of all residents, including vulnerable and marginalized populations. These strategies aim to address systemic inequalities and create more equitable and inclusive societies.
Social justice is fundamental to achieving equality in human geography. It emphasizes the fair distribution of resources, opportunities, and power within society, aiming to address systemic injustices and promote the well-being of all individuals and communities. Social justice principles guide efforts to challenge and transform discriminatory structures, policies, and practices to create more equitable and inclusive societies.