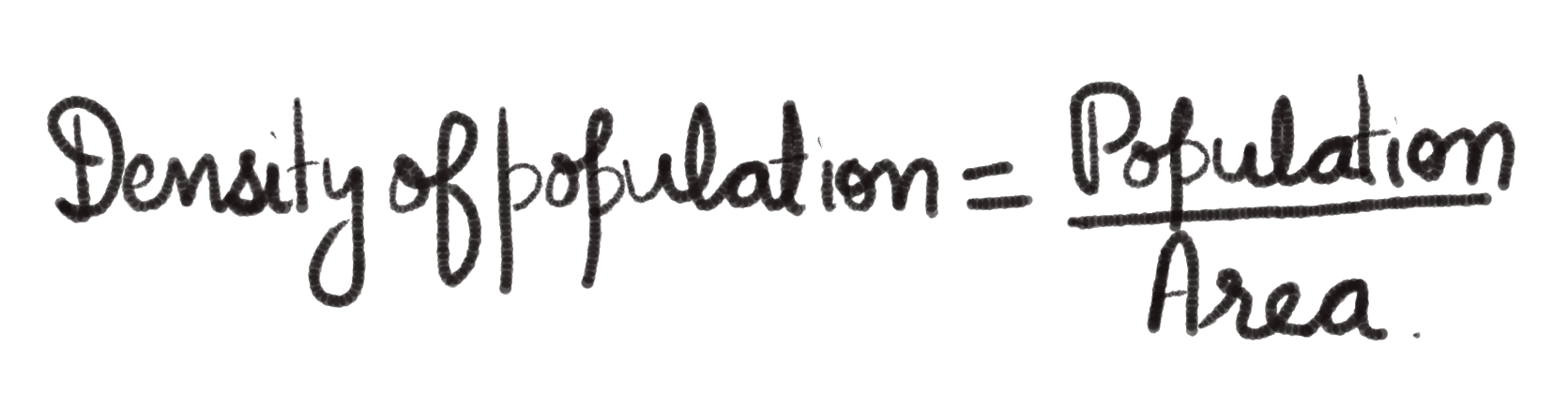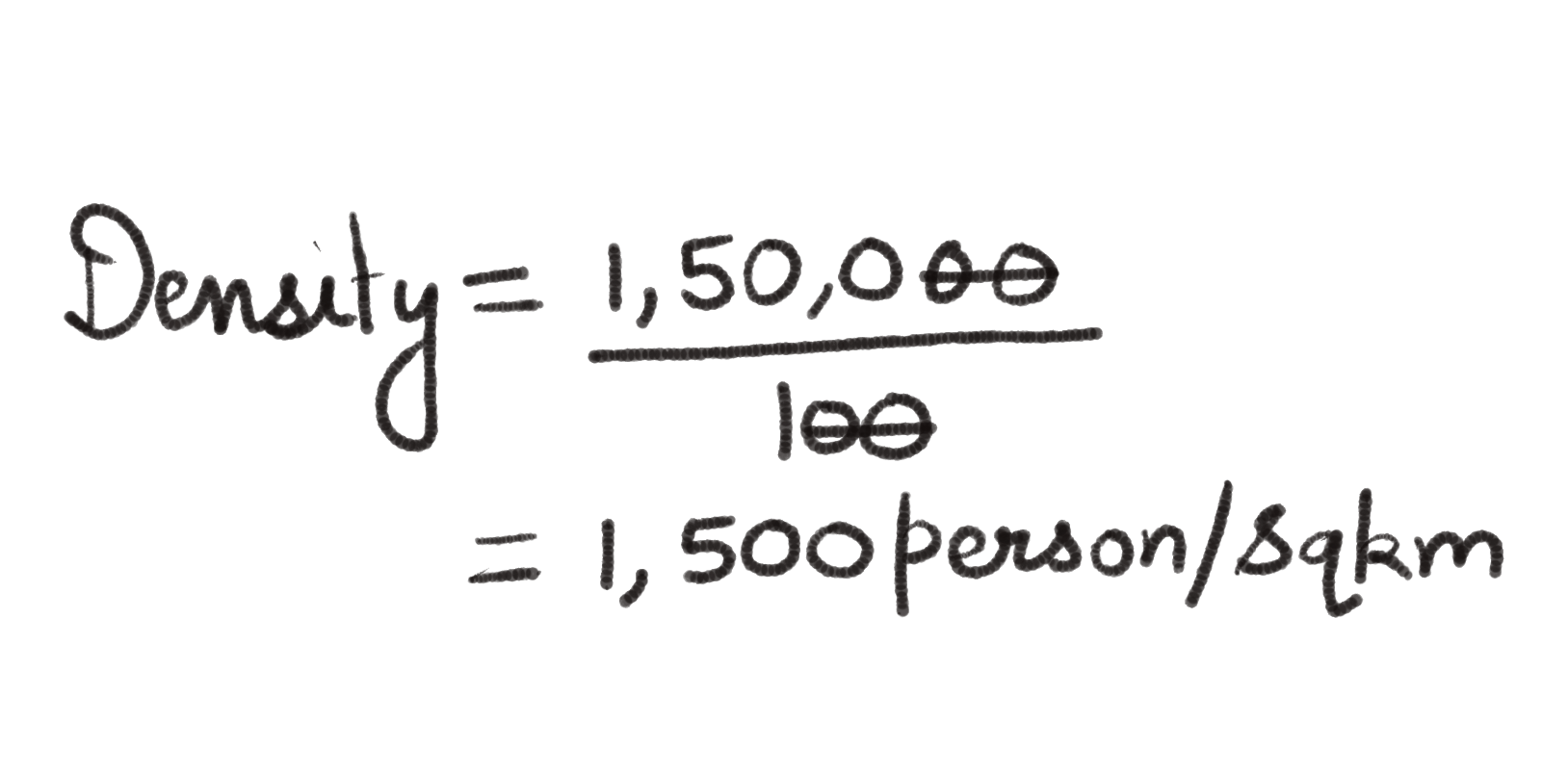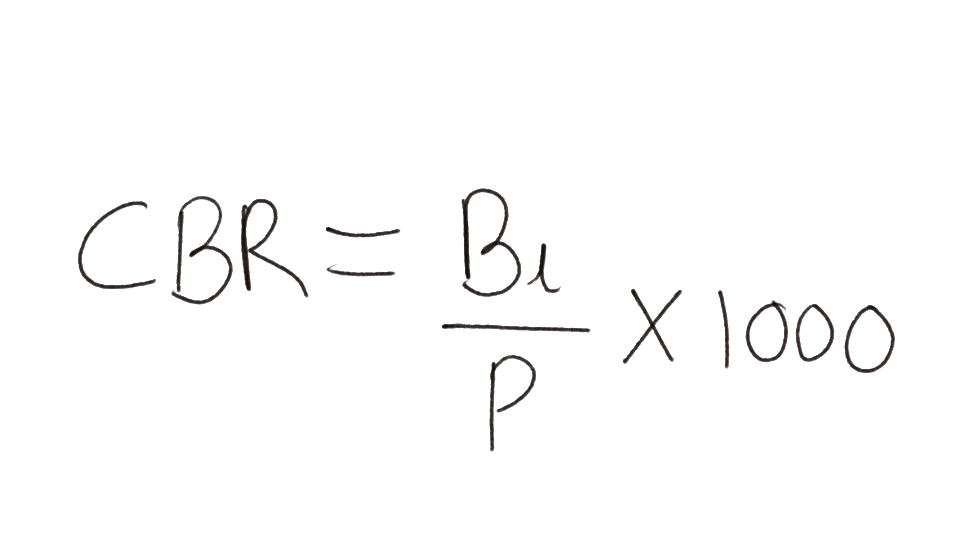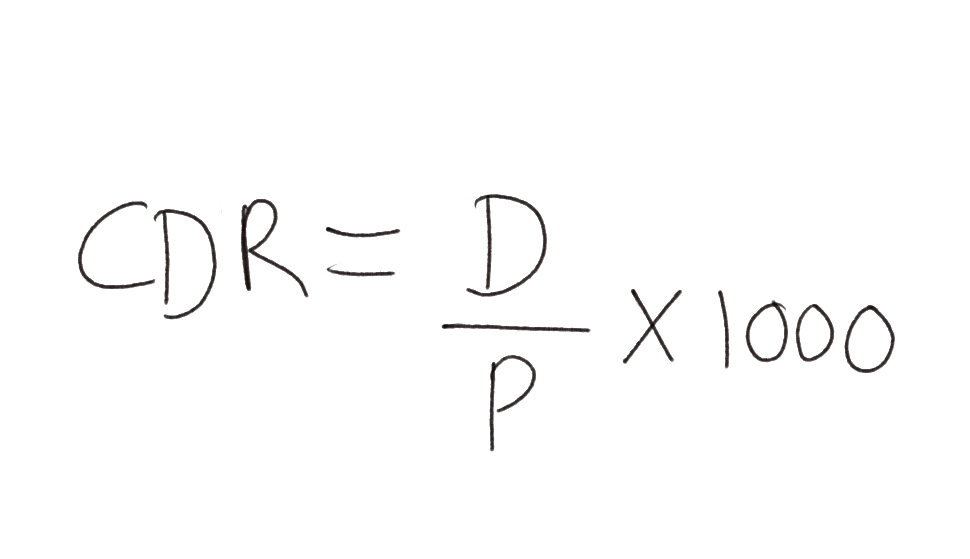The people of a nation are its true wealth. It is they, who are the real resources and make use of the country’s other resources and determine its policies. Conclusively a country is identified by its people.
It is necessary to know how many men and women a country has, how many children are delivered each year, how many deaths occur and how? Whether they reside in cities or villages, can they read or write and what kind of occupation they have? These are what you will study in this article. The world at the beginning of the 21st century registered the attendance of over 6 billion population. Let’s study the patterns of their density and distribution here.
Why do people fancy living in specific regions and not in others?
PATTERNS OF POPULATION DISTRIBUTION IN THE WORLD
Models of population distribution and density help us to recognise the demographic features of any area. The term population distribution relates to the way people are apportioned over the earth’s surface. In a broad sense, 90 per cent of the world population exists in about 10 per cent of its land area.
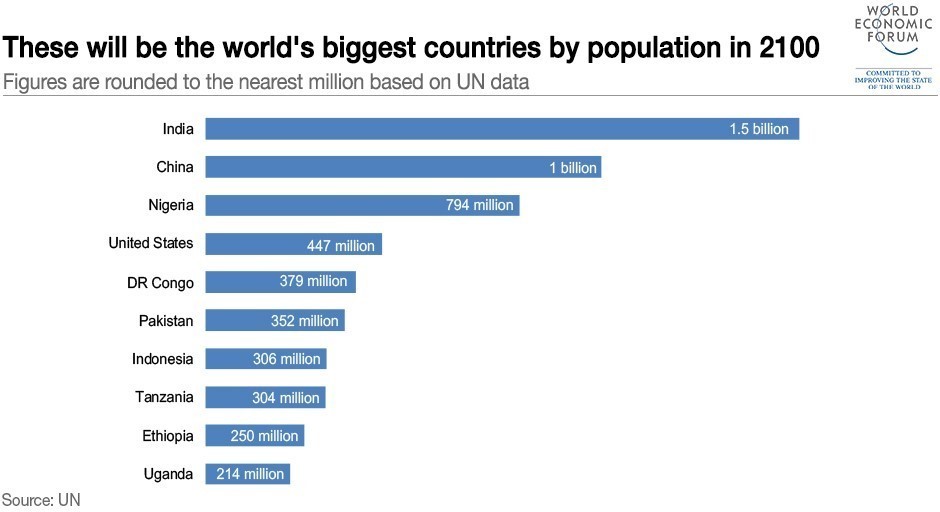
The ten most populated countries of the world provide about 60 per cent of the world’s population. Of these ten countries, six are found in Asia. Recognize these six countries in Asia.
DENSITY OF POPULATION
Each unit of land has limited potential to sustain people living on it. Hence, it is important to understand the ratio between the numbers of people to the size of the land. The ratio we get is the density of population. It is normally measured in persons per sq km.
For example, the area of Region X is 100 sq km and the population are 1,50,000 persons.
FACTORS INFLUENCING THE DISTRIBUTION OF POPULATION
I. Geographical Factors
(i) Availability of water: Water is an essential factor in life. So, people prefer to reside in areas where fresh water is readily available. Water is used for bathing, drinking, cooking and washing – and also for crops, cattle, navigation and industries. Therefore, most densely populated areas of the world mostly lie near river valleys.
(ii) Landforms: People prefer living on gentle slopes and flat plains. This is because such areas are agreeable for the production of crops and to develop roads and industries. The mountainous and hilly areas limit the development of the transportation network and therefore initially do not support agricultural and industrial development. So, these regions tend to be less populated.
The Ganga plains are one of the most densely populated areas of the world while the mountains in the Himalayas are scantily populated.
(iii) Climate: An extreme climate such as very cold or hot deserts are difficult for human habitation. Cities with a pleasant climate, where there is not much seasonal fluctuation pull more people. Regions with very heavy rainfall or excessively harsh climates have low population. Mediterranean regions were occupied from early periods in history due to their agreeable climate.
(iv) Soils: Fertile soils are critical for agricultural and associated activities. Therefore, regions which have fertile loamy soils have more people living on them as these can sustain intensive agriculture.
II. Economic Factors
(i) Minerals: Regions with mineral deposits lure industries. Mining and industrial activities create employment. So, skilled and semi-skilled workers migrate to these areas and make them densely populated. Copper belt of Katanga Zambia in Africa is one such excellent example.
(ii) Urbanisation: Towns offer better work opportunities, educational and medical amenities, better means of transportation and communication. Good public facilities and the appeal of city life attract people to the cities. It drives rural to urban migration and cities grow in size.
Megacities of the world continue to fascinate a large number of migrants every year.
(iii) Industrialisation: Industrial belts give job possibilities and entice large numbers of people. These involve not just factory workers but also shopkeepers, transport operators, bank employees, teachers, doctors, and other service providers. The Kobe-Osaka area of Japan is thickly populated because of the presence of several industries
III. Social and Cultural Factors
Some countries interest more people because they have religious or cultural importance. Similarly, people tend to move away from places where there is social and political unrest. Many times governments grant incentives to people to live in scarcely populated areas or migrate to some other area from overcrowded places.
POPULATION GROWTH
The population growth or population change relates to the change in a number of residents of the area during a specific period of time. This change can be positive as well as negative. It can be stated either in terms of absolute numbers or terms of percentage. Population change in an area is a critical indicator of economic development, social upliftment and historical and cultural history of the region.
COMPONENTS OF POPULATION CHANGE
There are three elements of the population change – births, deaths and migration.
The crude birth rate (CBR) is represented as the number of live births in a year per thousand of
population. It is calculated as:
Here, CBR = Crude Birth Rate
Bi = live births during the year
P=Mid year population of the area.
Death rate performs a vital role in population change. Population growth happens not only by rising births rate but also due to the declining death rate.
Crude Death Rate (CDR) is a simple means of estimating the mortality of any area. CDR is signified in terms of the number of deaths in a certain year per thousand of the population in a particular region.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors influence the distribution of population within a country?
Population distribution is influenced by factors like geographical features, climate, availability of resources, economic opportunities, and historical settlement patterns.
Define population density and explain how it is calculated.
Population density is the number of people per unit of land area. It is calculated by dividing the total population of an area by its land area (e.g., people per square kilometer).
What is population growth rate, and why is it significant?
Population growth rate is the percentage change in a population over a specific period. It’s significant because it indicates whether a population is increasing, stable, or decreasing, impacting social and economic planning.
Describe the concept of urbanization and its role in population distribution.
Urbanization is the process of increasing urban population. It leads to the concentration of people in cities and has a significant impact on population distribution trends.
What are some factors that contribute to high population growth in certain regions?
High birth rates, limited access to family planning, cultural norms, and healthcare disparities are factors contributing to high population growth in some regions.