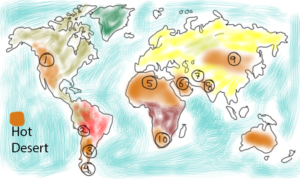
First have a look at one of the most famous hot deserts around the world.
- Great Basin Desert
- Peruvian Desert
- Atacama Desert
- Patagonian Desert
- Sahara Desert
- Arabian Desert
- Turkestan Desert
- Great Indian Desert
- Gobi Desert
- Kalahari and Namib Desert
Note – If you notice carefully, major hot deserts having extremely high temperatures are found near the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn.
World’s largest hot desert is Sahara which covers almost the whole continent.
With an extreme climate hot deserts have very challenging environment for living beings. You will hardly any kind of vegetation there. Only few plants and animals have adapted to live in this climate.
Climate of the hot desert
- Climate is extremely hot and temperature remains more than 40 degrees for most time of the day. However, the hot desert become cold as the temperature falls below 0 degree.
- Climate is very dry with negligible humidity. The average rainfall is 250 mm a year.
Soil
- Thin, sandy, rocky and grey are the terms to describe the soil of the desert. Since it is very dry, it soaks the rainfall quickly
- The crusty look of the surface is due to the lack of water in the soil. Due to high temperature the water under the surface rises up through evaporation and leave salts behind on the surface.
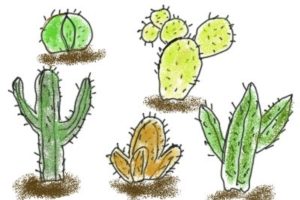
Plants in Hot Deserts
Most people would associate the desert with cacti and short bushes, which is definitely the reality of the plant life that can be found there. The plants that are in deserts are specially adapted to cope with very little rainfall and a lot of them have short life cycles. This means that they only grow when it rains.
If we take a look at some of the plants that can be found in deserts, then we can see that a lot of them have long roots or roots that are spread out. Plants with long roots can reach sources of water that can be found deep underground, while plants with wide roots can catch a lot of water when it does rain.
Animals in Hot Deserts
The animals that can be found living in the desert are worth paying attention to, because they are specially adapted to live there. They have to be able to thrive in such a harsh environment. When most people think about animals in the desert, they think about reptiles and insects.
Some mammals cope very well in the desert, but they tend to be very small and a lot of them are also nocturnal. This means that they do not have to cope with the extreme temperatures during the day, but they do have to cope with the cold at night. A lot of the birds that live in the desert leave the area when the temperature becomes too extreme.
People in Hot Deserts
Humans who live in the desert usually grow crops to sustain themselves, but they need to be near natural springs and wells in order to do this. Most of these bodies of water can be found along the very edge of the desert.
There are also indigenous people who call the desert their home, but they tend to be nomadic. They take herds of sheep and goats across the desert in search of food and water. This means that they cannot stop in one place for too long.
The Climate in Hot Deserts
Deserts are generally thought of as being places where very little rain falls. But, when rain does fall, it can vary a lot. You might only see rainfall once every several years in a desert. This is very extreme and it has led to a lot of plants in the desert having short life cycles that are prompted by rainfall. The temperatures in the desert are also extreme, being very hot during the day and very cold at night.
Desert Ecosystems
If you have not learnt about ecosystems, then you should take a look at our page that covers the topic.
In deserts, ecosystems are incredibly fragile. One simple change could affect a whole ecosystem. But, ecosystems in the desert have a lot of different things to content with. For example, the amount of rain that falls in a hot desert is very low. This means that animals have to keep moving to find water, or they have to be adapted to cope with very little water.
The people who live in deserts can also negatively impact ecosystems because of the way that they water the land that their crops grow on. Most of the time, this involves taking unsustainable amounts of water from underground. Naturally, this means that there is less water for the plants and animals who also rely on those sources.
Desertification
While a lot of the plants and animals in hot deserts are specially adapted to live there, there are still a lot of problems that you need to be aware of. Desertification is probably the biggest problem in the desert because it involves land degrading, meaning that it becomes less productive.
One of the key aspects of desertification is soil erosion. This means that soil can easily be removed in layers by gusts of wind and water. This leads to nutrients being lost and soil becoming less productive quickly, making it difficult to grow anything on it.
Reducing the Risk of Desertification
There are plenty of different things that can be done to reduce the risk of desertification, they include:
- By planting trees, people can prevent soil erosion. This is because the trees will act as windbreaks and prevent the wind from blowing away the top level of soil. Trees can also be used to provide crops and animals with shade, reducing the temperatures that they are exposed to.
- To reduce soil erosion, land that is used for agricultural purposes should occasionally be left to rest. This allows the soil to recover nutrients that would otherwise cause the land to become unproductive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the defining characteristics of hot deserts, including their extreme temperatures, arid conditions, and adaptations of desert flora and fauna?
Hot deserts are characterized by high temperatures, low precipitation, and specialized adaptations of plants and animals.
Explain the role of desert plants, such as succulents and xerophytes, in conserving water and thriving in arid environments.
Desert plants have adapted water-saving mechanisms like modified leaves, reduced transpiration, and deep root systems.
Describe the unique behaviors and physiological adaptations of desert animals, including nocturnal activity, water storage, and thermoregulation.
Desert animals have evolved to conserve water, regulate body temperature, and adapt to limited food resources.
Human habitation in hot deserts requires efficient water management, and sustainable development involves reducing environmental impacts.
How does climate change impact hot desert ecosystems, including shifts in desert boundaries, increased desertification, and potential implications for global climate patterns?
Climate change can lead to desert expansion, increased desertification, and disruptions in local and global climate systems.