Download the GCSE Geography Natural Hazards: Tropical Storms Resources module
This module contains:
- An editable PowerPoint lesson presentation
- Editable revision handouts
- A glossary which covers the key terminologies of the module
- Topic mindmaps for visualising the key concepts
- Printable flashcards to help students engage active recall
- A quiz with answer key to test knowledge and understanding of the module

Natural Hazards: Tropical Storms
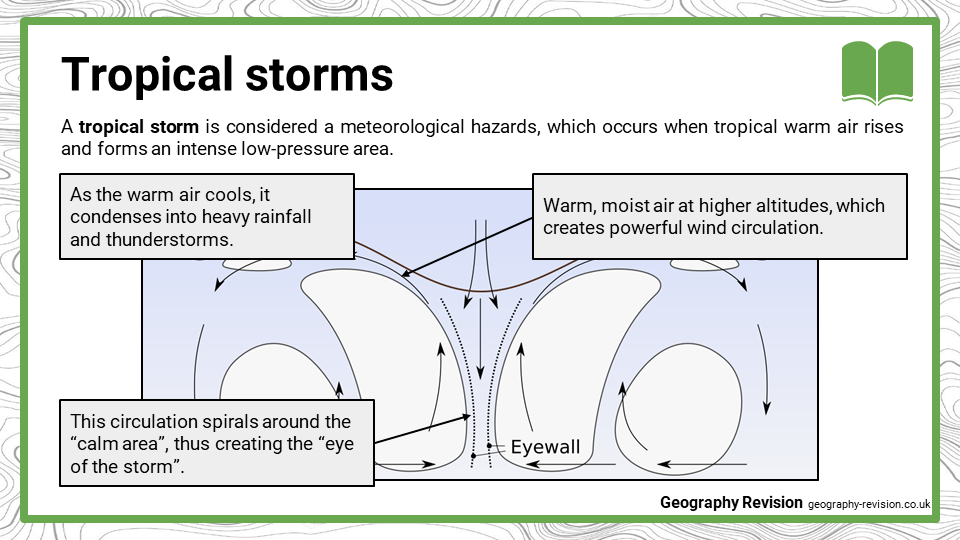
A tropical storm is considered a meteorological hazards, which occurs when tropical warm air rises and forms an intense low-pressure area. As the warm air cools, it condenses into heavy rainfall and thunderstorms. Warm, moist air at higher altitudes, which creates powerful wind circulation. This circulation spirals around the “calm area”, thus creating the “eye of the storm”.
This GCSE Natural Hazards module introduces tropical storms to your students, explaining:
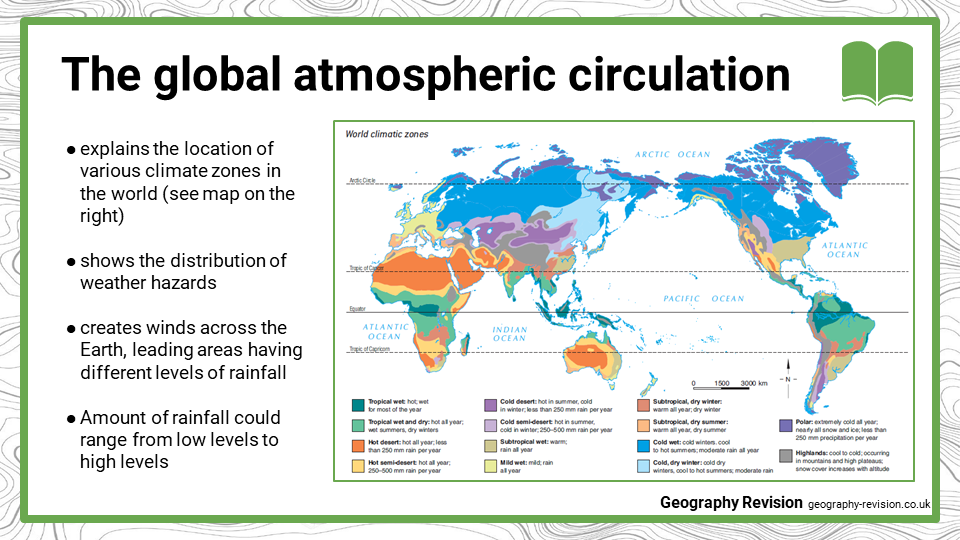
- What does the global atmospheric circulation try to explain? How does latitude influence variations of climate zones in the Earth?
- How do meteorologists collect weather data? What are the instruments used in performing weather data collection?
- What are the different weather elements and the instruments used to measure these?
- How are tropical storms formed?
- What are the characteristics of a tropical storm? How frequent are tropical storms? Where are they located?
- What are the effects of tropical storms on people and the environment?
- What are the causes, impact, and management strategies for extreme weather events in the UK?
- What happened during the flash flood event in Boscastle in 2004?
What are the responses by MEDCs and LEDCs to tropical storms?
More Natural Hazards Modules
Tropical Storms is one lesson in our Natural Hazards module. The other theory lessons can be found below: